Simulation of smart grids with embedded communication
The inclusion of a wide range of different components such as controllers, sensors, and actuators, has made the management of modern smart grids more complex. The coordination of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) combined with storage systems is another necessity in the future of power generation. Due to this increasing use of smart components in smart grids, interoperability among them is a crucial aspect to address. To achieve optimal performance of all grid components, they are interconnected through a communication network, allowing control in a distributed system and a decentralized manner. IEC61850 is a communication standard that has been already used in substations because of its instant data transfer and the ability to enable data exchange between a variety of smart energy-related digital technologies.
The goal of this activity is to recreate a given substation using built-in IEC61850 protocols instead of conventional co-simulations and to study the performance of this more realistic architecture. The application of the communication protocols defined by the IEC61850 standard in Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) by using a prototype testbed architecture running on a real-time digital device has been examined in this project.
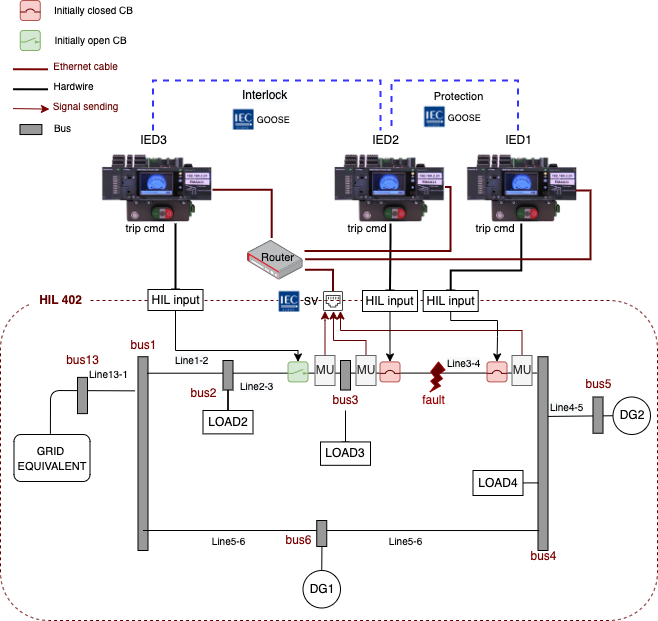
This testbed includes the supervisor, the substation bus, and the process bus communication layer creating a local network exchanging data at distinct levels. This architecture is implemented using Intelligent Electric Devices (IEDs). Three communication protocols in IEC61850 standard are adopted in different layers of the architecture (Fig3). The outline of one of the implemented scenarios using this testbed is depicted in fig4.
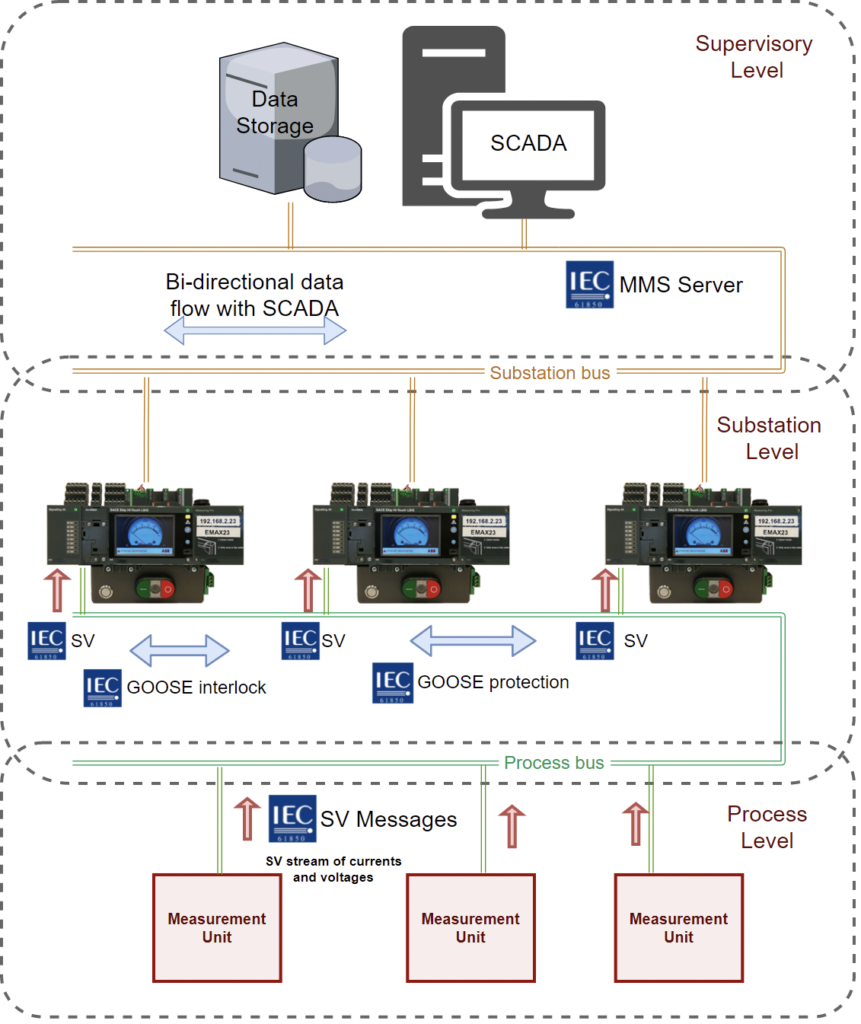
MMS server: supervisory level
GOOSE messages: Substation level
SV messages: Process level
